People love their pets. That’s obvious not merely in our impulse to anthropomorphize them but to increasingly care for them the same way we do human members of our families. American pet owners used to really only took their pets to clinics to treat obvious physical symptoms, but they’ve increasingly been hitting up the vet […]
[IDXX – IDEXX Labs] Priced to Win
Posted By scuttleblurb On In [IDXX] IDEXX Labs | Comments Disabled[MSFT – Microsoft] Death Star, Reformed
Posted By scuttleblurb On In [AMZN] Amazon,[GOOGL] Alphabet,[MSFT] Microsoft | Comments DisabledThere’s a good reason why Microsoft was dubbed the Death Star by many fearful detractors during the on-premise era: its OS/application stack, with 90%+ desktop share, was an impermeable force that whipped the surrounding computing galaxy into submission. Given Window’s ubiquity, value added resellers and systems integrators optimized their resources and relationships by supporting Windows […]
[SERV – ServiceMaster; ROL – Rollins] Scale Economies and Hard Realities: Part 2
Posted By scuttleblurb On In [ROL] Rollins,[SERV] ServiceMaster | Comments DisabledCountless termites die every day from natural causes, and that makes them the lucky ones. Many are poisoned by liquid pesticide sprayed along entry routes into homes. Still others are duped into ingesting toxic morsules that they share with nest mates, unwittingly wiping out whole colonies, slowly, over months. More creatively (and less commonly), they […]
[TRUP – Trupanion] A SaaSy Underwriter
Posted By scuttleblurb On In SAMPLE POSTS,[TRUP] Trupanion | Comments DisabledLooking at TRUP is like staring at one of those ambiguous images that could be both a rabbit and a duck, both a saxophonist and a woman’s face: we know that this is an insurance company, but we’re compelled to analyze it as a data-driven subscription service.


Of course, all responsible insurers are data-driven and the recurring nature of premiums also make them subscription-like, but we don’t typically think of insurers as a subscription service in the same vein as a SaaS enterprise. We do for TRUP largely because its management team has diligently trained us to focus on SaaSy metrics. Some of this is just reframing vocabulary: “subscription fees” not “premiums”, “members” not “policyholders”, “Territory Partners” not “agents”.. Trupanion’s ignorance of the insurance industry lexicon – scarcely a mention of reserves, underwriting leverage, medical cost trends, book value – is so obtrusive as to almost certainly be by design (what fast-growing enterprise wants to be seen as a boring insurance company?).
But this is also the first insurer I’ve see that disaggregates retention by member cohort and discloses lifetime value to customer acquisition cost ratios. That’s not a knock on the company. The first principle to any recurring, subscription-like model, insurance company or not, is onboarding customers for far less money than those customers will generate in lifetime profits. With most of the stuff you buy – a haircut, an iPhone – there is little confusion about the value of the product to you. Insurance is a lot squishier because you don’t know at the time of purchase whether you’ll need it. For major categories of insurance – where the covered thing is monetarily significant and its cost readily determinable, as in the case of a car or house, or where it transcends monetary value, as in the case of your family’s health – we easily buy into the collective understanding that in any given year, the premiums from those on whom fortune smiles subsidize those on whom she frowns. We don’t feel like our rights are being trammeled when law mandates we buy such insurance or that we’re being bamboozled when our insurer earns an underwriting profit from this scheme. We’re risk averse and understand that peace of mind is worth paying for and that an insurer should be compensated for giving it to us. But dogs and cats?
While there’s no question that we treat our pets far more humanely than we used to and that pets have graduated from the status of mere property, they still don’t occupy the same sanctified hemisphere as humans and we’re far from consensus on the range of seriously unfortunate health outcomes that we should be willing to prepare for. If you ask your friends about pet medical insurance, as I did, you’ll likely find that only a few have it, maybe half think it a reasonable purchase and the rest may outright scoff. Rather than pay $50 for a Trupanion policy with a 10% deductible, why not just put $40 in the cookie car every month as a sort of pet health savings account? If I’m shelling out $600 this year for a Trupanion policy and eat 10% of the costs, I need to think there’s a 20% chance of at least $6,000 in medical emergencies in the next 12 months for the policy to be “worth it”. [to put that in context, treating hip dysplasia for a Golden Retriever can cost anywhere between $2,000 (if diagnosed early) and $5,000 (if diagnosed late and a hip replacement is required)].
Of course, the decision to purchase insurance can be an emotional one that goes beyond sterile expected value calculations, and the more importance you place on your pet’s life and comfort, the less willing you are to roll the dice…but the point is that on the surface, it’s not entirely clear to me pet owners feel they need insurance for their pets. But can they be made to think they need it? There’s some evidence to believe that they can: the number of pets covered by Trupanion has compounded by 25%/year since 2011 to over ~360k and nearly 85% of members renew their policies every year…and half the lost profits of those who don’t renew are offset by existing members who insure more pets or refer their friends. The proselytizing efforts begin with the 40,000+ vets staffed at the 28,000 vet hospitals across North America (20,000 of which are independently owned and operated) who deliver ~54% of TRUP’s new members and from whom pet owners seek trustworthy guidance. [According this recent Motley Fool interview [4], Trupanion’s CEO claims that when vets recommend Trupanion to their clients, 1 in 4 people enroll.]
Sometimes oblique coverage restrictions, annual payout caps and long waiting periods for covered treatments are buried in fine print; other times, the insurance company and the vet charge based off different fee schedules, with the pet owner paying for the entire procedure out-of-pocket based the vet’s fee schedule only to be reimbursed weeks later by the insurance company using a lower “usual and customary” rate [which is based on fees charged by other physicians in the surrounding area for the same procedure]. A vet probably won’t be blamed for not proactively recommending pet medical insurance, but pushing a policy that culminates in an expensive “gotcha” moment is poison. Trupanion attacks these causes of friction and confusion by:
1/ pricing off the cost of care. Trupanion carefully estimates the cost of medical care across 1mn+ dimensions – species, breed, zip code, deductible, age – and simply tacks on 30% to arrive at the policy price paid by the pet owner…so, a pet owner is basically paying a 30% premium above expected medical costs to rid herself of cost uncertainty. Trupanion then pays out 90% of the vet’s invoice, with no limits per claim or illness. So, it doesn’t matter if one vet charges $2,000 and a rival vet across the street charges $1,000; Trupanion will cover 90% of the eligible treatment cost in both cases. Assuming Trupanion has accurately estimated the cost of care, in aggregate, 70c of every premium dollar Trupanion collects goes to paying vet invoices;
and
2/ re-directing reimbursement flow (in progress). With traditional pet insurance, the patient covers the entire vet invoice upfront and then hopes the check that arrives from the insurer in 2 weeks will reimburse her for the “right” amount. While most of Trupanion’s claims are still paid via check, they are increasingly routed through Trupanion Express, in which Trupanion pays the vet 90% of the bill directly, thereby taking the burden of up-front payment away from the consumer. Express can be integrated into practice management software so that an invoice is immediately shot over to Trupanion, who wires the requested funds into the vet’s bank account in less than 5 minutes. The number of vet hospitals with Express installed has grown from 89 in mid-2014 to 500 in 2015 to ~1,300 today, with over 30% of vet invoice dollars channeled through Express, on its way to 95%+. No other competitor in the space is even bothering to pursue a similar direct payment scheme.
These two changes largely lift the confusion attending discrepant pricing schedules and alleviate the strain of what in some cases could be an enormous immediate upfront payment for the pet owner, followed by an anxiety-ridden reimbursement interval. The member knows his out-of-pocket burden from the get-go and will not be financially surprised down the line. And because a Trupanion member need not wrestle with the financial uncertainty of costly medical care, she spends twice as much on vet services over her pet’s life than an uninsured pet owner…and the vet can simply focus on recommending the best treatment, without also stressing over the owner’s ability to pay.
Even so, considering the history of disappointing experiences with pet medical insurance, it’s no wonder that winning over vets has proven a laborious process. It can take 3-5 visits for a Territory Rep to even get her first meeting…so, if the TR is making 1 visit every 6 months, we’re talking years. Trupanion makes close to 100,000 face-to-face vet visits every year, with 200 hospitals per territory visited every 60 days (with touch frequency now increasing with impending account manager build out), and even after hammering away at vet conversion for nearly a decade in the US, the company still has significant work ahead: against a universe of 25,000 addressable hospitals in the US, only 8,100 are actively recommending Trupanion today, a figure that is growing by ~500-600 hospitals/year. Competitors, on the other hand, continue to take a direct-to-consumer approach, carpet bombing their territories with online marketing to create awareness, which in the absence of vet buy-in has not proven very effective.
Building trust is a time consuming process that requires TRs to persistently contact vets, who must then observe positive customer experiences firsthand. These relationships cannot be bought, but must be earned over time: a vet hospital will not compromise a pet owner’s continuing business for referral fees and besides, Trupanion does not offer kickbacks of any kind to vets for referring patients. You may be surprised to know that with the exception of VPI Nationwide, the largest player in the space with 40% share (vs. #2 Trupanion with 20%), other competitors like Healthy Paws and Pet Plan don’t underwrite the policies they sell. Trupanion’s conceit is that by owning all links in the chain – from sales to underwriting to claims processing to customer service – and forgoing reinsurance, it can provide insurance at a ~20% lower cost than peers. These savings are used to cover a greater proportion of claims costs – 70% of premiums at Trupanion vs. closer to 50% for peers – enabling a “no-fuss” payments experience that induces greater satisfaction from pet owners (who remain Trupanion members for longer) and buy-in from vets (who feel comfortable enough to recommend Trupanion to new clients).
Of course, sustainably profiting off a cost-plus model and credibly delivering on the promise to immediately cover 90% of whatever invoice requires precise, granular insight into the cost of pet acquisition and medical care. Over 17 years since inception, with data from 1.5mn+ claims and over 500,000 invoices/year, Trupanion has amassed cost and retention experience across 1mn+ category permutations…so, for instance, the company understands how the claims experience of a 5-year old bulldog in zip code 11201 differs from that of a 3-year old Shih Tzu in 60047 and can price the two pets accordingly. There are no short cuts to this process. The time required to build claims experience and flesh out statistically significant patterns at such a granular level is a steep learning curve that even a well-funded competitor cannot easily surmount. Although VPI Nationwide has been around longer than Trupanion, their dataset is less robust because they don’t price their policies with nearly as many observations (zip code, for instance) as Trupanion, nor do they cover congenital and hereditary conditions. [to be clear, Trupanion doesn’t cover pre-existing conditions either, but unlike other insurers, it doesn’t refuse coverage on all future illnesses arising because of pre-existing conditions].
Still, while data may be a competitive advantage in the early stages of penetrating a market niche, I’m not sure this in itself constitutes a real moat. Data has to be proprietary, valuable, and part of a self-reinforcing process (data network effects) for it to count as a sustainable edge. There’s a reason why you never hear insurers tout data as a unique advantage…there are diminishing returns to data as the relationship between price and insured risk doesn’t change all that much for granular exposures and eventually becomes common knowledge.
(the Lifetime Value of a Pet (LVP) to Pet Acquisition Cost (PAC) ratio that Trupanion reports every quarter is the blended output of explicit LVP:PAC targets across a slew of subcategories. So, while the lifetime value of, say, a 2-year old cat in Manhattan with a $1,000 deductible will differ from bulldog puppy in Pittsburgh with no deductible, Trupanion can toggle pricing and acquisition spend to get iteratively closer to a common IRR across subcategories, with no cross-subsidization between them. Ideally, the table would look something like this…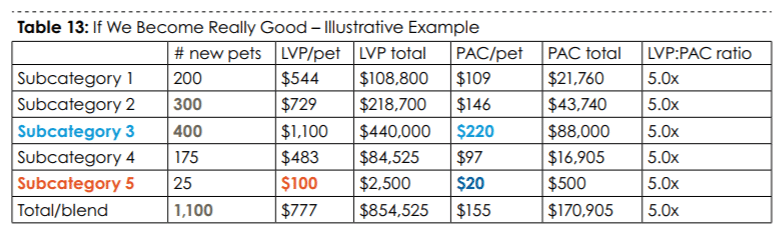
Not. quite. there. yet…
…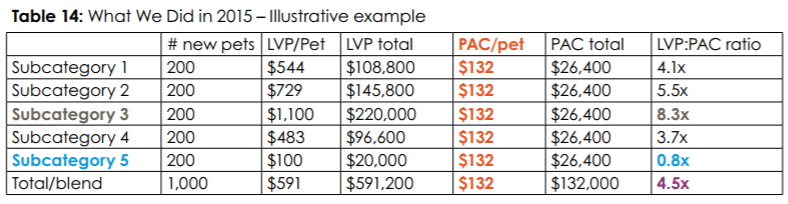
(Tables 13 & 14 from Trupanion’s 2016 Annual Letter)]
Meager pet insurance adoption rate in North America (< 2% of ~180mn dogs and cats) compared to certain Western European countries (25% in the UK, 50% in Sweden), is an oft-touted part of the bull case. Of course, one wonders why, when pet insurance has been available in America since at least the mid-80s, the disparity exists in the first place? I don’t really know. But one reasonable-sounding explanation I’ve heard is that in Western Europe, pet insurers launched by first winning over vets and those vets then pushed the product to consumers…whereas in the US, insurers started by asking “what price will pet owners pay for this thing called ‘pet insurance’?” and then reverse engineered a product without consulting the vets, yielding something that both consumers and vets hated.
In any case, it doesn’t really matter. I think we just want to see that the method to driving category adoption is sound. In an embryonic market, it’s up to pioneering companies to create the category. Pet medical insurance is so nascent in the US that although Trupanion continues to claim share – there are around 20 brands that make up the pet insurance space, but 2 players, VPI Nationwide and Trupanion, account for 60% of the insured pets – it does so in a market that, against the broader population of insurable pets, barely exists. Rather than look to foreign countries for cues, it seems better to just make a judgment call on whether a) the value proposition for vets makes sense, b) the company has the will and wherewithal to push the ball forward, and c) the product, when discovered and used by the end consumer, solves a real need (including a need the consumer previously didn’t even know she had). a) and c) are tied at the hip since, as previously discussed, vets will only pitch Trupanion if the pet owner perceives benefit. While I harbor doubts about the intrinsic value to a pet owner, those personal reservations are trumped by nearly a decade of data strongly supporting the claim that yes, pet insurance is becoming a thing in the US. As born out over many cohorts, the average life of a Trupanion member is around 6 years…
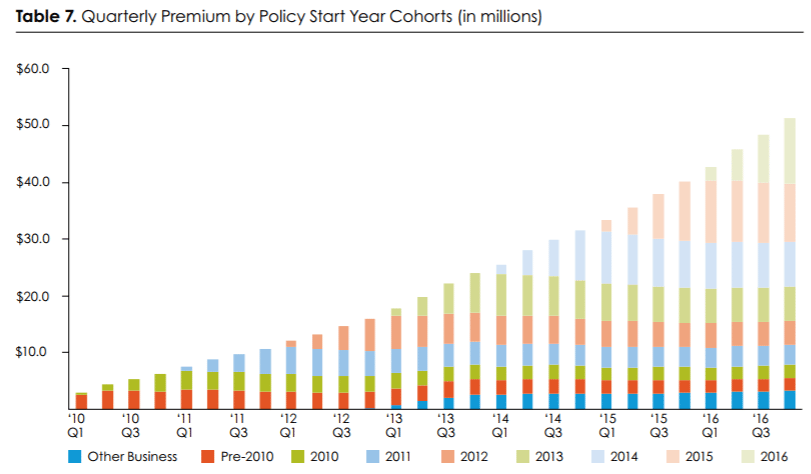
…during which period the company pulls 20c in variable profit from every incremental premium dollar, reinvesting most of that into acquiring new pets…
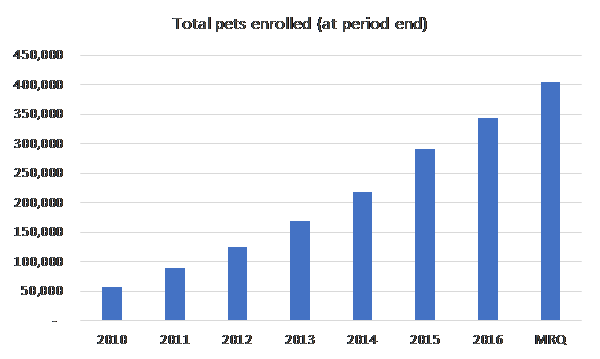
….at compelling lifetime values translating into huge IRRs, leveraging sales & marketing and fixed expenses along the way.
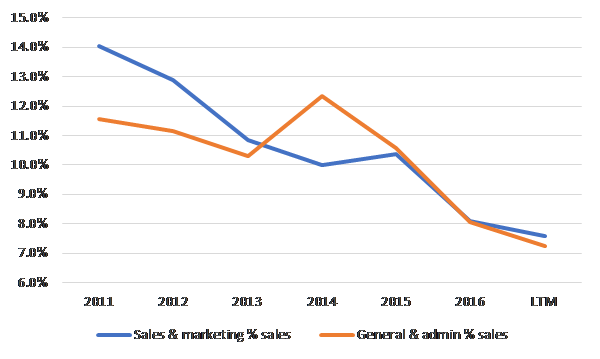
The IRR math works roughly as follows: on average, Trupanion pays $175 to acquire a pet and recognizes premiums of around $53 for that pet each month over 71 months. That 53 bucks is whittled away like so:
Monthly premium: $53
Vet invoices: ($37) [70% of the $50 premium]
Variable expenses: ($5)
Contribution profit: $11 [20% of premiums. The Lifetime Value of a Pet (LVP) is computed off this figure]
After adding back sales & marketing, Trupanion’s trailing 12 month EBITDA margin after stock-comp is ~8%, implying fixed costs of ~12% of premiums [20% contribution margins less 8% EBITDA margins ex. sales and marketing], so 60% of contribution profits are being consumed by fixed operating costs at the moment.
But at scale, which management pegs at ~700k pets (vs. over 360k today growing low/mid-teens y/y), the company thinks it can do 15% adjusted operating margins excluding the cost of adding new pets. When we back off 1%-2% for stock comp, it’s maybe more like 13%. Given the degree to which Trupanion has leveraged its cost structure over the last 6-7 years, I find this claim credible.
And so, at scale…. .
Fixed expenses: ($3)
Capital charge: ($0.6) [8% x (monthly premium divided into a premium:surplus ratio of 6x)]
Profit/pet/month: $7 [13% of premiums]
In other words, the company is generating ~$520 in profits over the average lifetime of a member, around 3x the cost to acquire that member. The cash flow streams over ~71 months impute a 65% IRR. Alternatively, at a 15% discount rate, the present value of cash flows over of a subscriber’s life is ~$330, nearly twice the cost of acquisition. Imputing attractive unit economics, of course, requires a sufficiently wide LVP-PAC spread. The $175 pet acquisition cost that I am using assumes the current LVP/CAC of 4.5x, where it has roughly been for the last 5-6 years. This figure would have to decay to below 2.5x before the NPV of pet acquisitions turns negative (i.e. destroys value).
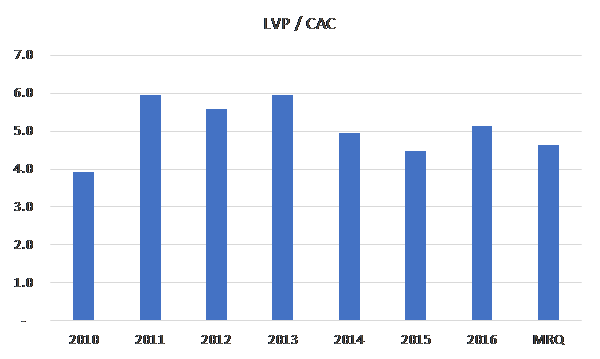
But I see no reason to expect such a draconian deterioration and in fact, it’s possible that as the company further densifies its markets with vet allies, layering on radio and TV spend may even boost conversion from vet recommendations, as has been true thus far in Trupanion’s mature markets where half or more of vet hospitals actively recommend Trupanion.
Given the unit economics and the runway, it’s not hard to see how things can get interesting [though whether they can get interesting enough to buy the stock at today’s valuation is an entirely different question]. Assuming today’s annual PAC spending of ~$15mn/year grows by a few million per year and even assuming LTV/CAC deflates to below 4x, I can get to just over 800k enrolled pets in year-7, around 12% growth per annum. Absent some “silver bullet for cost effective accelerated organic growth” (company’s words), management seems determined to fund its expansion entirely with internally generated profits.
Applying a pre-PAC scale margin of 13% to implied revenue gets us to around $70mn in pro-forma EBITDA, which, assuming reinvestment, will be growing by low-teens, providing still more ammo for pet acquisition. With 800k enrolled pets against a universe of 180mn dogs and cats in North America, Trupanion will still not have even nicked the surface of its potential…so, still be plenty of opportunity to deploy maybe 40%-50% of pre-PAC EBITDA into onboarding pets at 40%+ IRRs. In theory at least. What you’ve just seen is the rabbit. But what about the duck?
After all, this is still an insurance company and balance sheet strength reigns paramount. But is it and does it? Trupanion’s underwriting leverage – premiums to surplus ratio, a measure of how much underwriting risk you are assuming relative to the capital you hold – is greater than 6x [Trupanion does not reinsure its risk, so subscriptions = gross premiums = net premiums]. Whether this exceeds the standard of prudence depends on the nature of risk being insured. Typically, a ratio greater than 3x is considered unusually aggressive for a P&C underwriter and an insurer with significant high-severity natural catastrophe exposure will keep it closer to 1x. Health insurers, in contrast, will underwrite 7x+ their surplus. In my experience, growth and conservative underwriting are hardly ever simultaneously executed well together, and if this were a run-of-the-mill P&C underwriter, Trupanion’s thin capital base would probably be reason alone to pass.
But I think Trupanion is a different animal. The risks covered under pet medical insurance are bite-sized and absent a major, widespread health contagion, uncorrelated. Agglomerating hundreds of thousands of claims results in a more predictable range of experiences from year-to-year at the population level than most traditional P&C exposures and with far less tail risk too. Given the highly granular, uncorrelated nature of the insured risks, catastrophe is a remote risk. The company’s exposures are also short-tailed, meaning that claims-triggering events are readily apparent and the costs from those events accurately estimable and paid soon thereafter: over 90% of the company’s reserves as of 3q17 are related to activities incurred in 2017 and close to 95% of claims paid over the last year was related to business underwritten in the same year. Only a miniscule amount of claims incurred and paid relate to prior years. [one negative consequence to premiums heading out the door to pay claims almost as soon as they come in is that Trupanion doesn’t benefit from “float” income as a typical insurer does].
Compare this to the “long-tail” risk of asbestos, where the health consequences from exposure remained latent for many years and claims were still being paid more than decade after policies were originally underwritten…that is, people were getting silently screwed by asbestos during the coverage period; the insurance companies didn’t know it at the time and so didn’t properly reserve for it. In contrast, the short-tail nature of Trupanion’s risk means that its best guess about claims cost and frequency is rapidly (in)validated and any deviations can be dynamically accommodated through price adjustments. While Trupanion won’t hike a member’s monthly subscription fee based on her pet’s individual medical condition, it will do so if the average cost of care for all pets within the same sub-category rises, so systematic pricing errors are quickly rectified. Steering the ship is 48-year old founder, CEO, and ~8% owner Darryl Rawlings, who has a good story about how his parents’ experience about not having the money to remedy a life-saving procedure for his childhood dog, prompted him to start Trupanion 10 years later (maybe too good a story?). In any case, I highly recommend reading his annual letters, which are refreshingly exorcised of hygienic corporate bullshit and lay out Trupanion’s operating strategy with a useful degree of granularity. Darryl seems authentically enthusiastic about this pet insurance mission and appears to “get” how value is created…it’s hard to imagine a diversified underwriter/bank/savings institution like Nationwide pursuing this opportunity with the same single-minded vigor.
[FSV – FirstService; CWD LN – Countrywide plc] Scale Economies and Hard Realities: Part 1
Posted By scuttleblurb On In [CWN LN] Countrywide plc,[FSV] FirstService | Comments DisabledToday’s post is part of a broader discussion about scale advantages: when they apply and to what degree. I’m addressing this topic in the context of rolled-up entities because, in my experience, it is here that scale advantages seem far too liberally promoted, even if they do sometimes apply with awesome effect. This write-up was […]
Blurbs [Online travel, B2B2C implementation]
Posted By scuttleblurb On In Podcast Blurbs | Comments DisabledExecutive Roundtable: Street Talk (11/9/17), Phocuswright Conference
Rachael Rothman, Sr. Analyst, Gaming, Lodging, and Leisure at Susquehanna Financial Group
(on hotel demand)
“I think we know from the industry-wide data that there is a definite shift to book direct…I would also just highlight that going back 30 years from hotel school, we always thought of brands as occupancy insurance and now that we’re getting 92 months into the recovery, I think you’re going to see that brand power come back into effect, and you’ve seen some of the hotel owners that have moved away from branded product and that relied on things like Expedia and Priceline actually suffer and underperform. And so I think it’s being proven out to the owners and to the operators that the brands actually are working and scale is working. Occupancies are at all time highs in the hotel industry, my stocks are at all time highs, and there are no signs [of] waning demand…there’s not a ton of pricing power but it isn’t a demand issue.”
(on hotels possibly filling the OTA gap on meta spend)
“They are unlikely to step in to fill that gap. I think historically that has not necessarily been a customer that they wanted. I view it as someone who’s pretty brand agnostic and price sensitive. I think what you could see though is some of the bigger brands stepping in with something like Instagram and Facebook and saying ‘hey Rachel, I see that you’re celebrating you’re 10-year wedding anniversary at the Ritz Carlton in Naples…how about next year you go to the Ritz Carlton Dana Point and you book today and we give you 20% off’. They already know I’m a loyal Ritz Carlton customer, they can see that I’m taking photos and interacting…and they can go direct to the customer with a targeted offer.”
(on alternative accommodations)
“First, there is some thought that it takes away pricing power on compression nights. So, that would be if you had SXSW in Austin, TX for example, historically maybe you could have raised your room rate by 30%, now you can only raise it by 10%. But, we also have to consider that Airbnb’s supply is flexible, meaning that people put their capacity on when rates are the highest and I personally am of the belief that Hilton and Marriott and their owners’ balance sheets are built for a recession. When we go into a recession, the Airbnb owners, many of them have extended themselves into having multiple properties and when they find that they can only rent that home for 30 bucks and it’s either $100 or 5 of their own hard labor hours to clean it, you’re going to see a lot of that capacity come off the market and I think it’s going to be the same balance sheet lesson that a lot of individual homeowners learned in the 2008 recession.”
(on loyalty discounts from hotel chains)
“I think it’s working, I think it’s a big deal…Expedia may be able to offer you a free flight or free whatever, what they can’t offer you is 9am check-in, 4pm check-out, free breakfast, unlimited free cocktails, any sort of amenity that any one of these hotel owners or operators can offer to their customers.”
Lloyd Walmsley, Managing Director, UBS
(on OTAs pulling back on meta)
“Priceline has been the most vocal about pulling back and they had spent a lot of money on trivago over the last 2 years and I think trivago was pushing pretty hard and you have a new management team come in and decide to take the strategy a little more aggressively. They had been funding a competitor in search channel so I think it makes eminent sense to try to reset that auction. Priceline has spent some money in TV historically but booking.com’s brand in all of our survey work has still lagged that of peers, so I think it makes sense to be building a brand…I think Google is going to continue to move further and further into the travel vertical and that poses obvious risks if you don’t have a strong brand.”
(on TV spending)
“[TV spending] makes the online spend more efficient. So, Google obviously has a quality score and the higher your click-through rate is the less you pay for ads. Kayak, when they were public, gave us enough disclosure as part of the IPO process that we could see when they started ramping their TV spend, in the first two years after they ramped their TV spend, the cost that they had to pay for their digitally acquired clicks was cut in half. I wouldn’t expect the same magnitude for a brand as big as booking.com but there are secondary benefits to being on TV.”
Eric Sheridan, Managing Director, UBS
(on loyalty discounts from hotel chains)
“Phocuswright put up a lot of their own data saying that loyalty rewards don’t actually drive as much velocity of shopping in travel. We’ve done consumer intention surveys that say similar things. The business market seems like it’s much more driven by loyalty rewards than the consumer marketplace…I would expect over time that the OTAs and maybe Airbnb explore loyalty and rewards.”
(on Amazon, Facebook, Google getting into travel)
“Amazon’s tried a couple times at this more in beta mode and never really gotten much further than that…I think that the inventory is so fragmented on a global scale that in order to achieve scale, I think it would take quite a long time to achieve the scale benefits that Expedia and Priceline have on the inventory side. We’ve always been fairly dismissive of the concept that Google will become an OTA. Google wants more of their partners’ marketing budgets by delivering more qualified leads and delivering more CPCs from it. So, from our view, Google’s always wanted to own more top-funnel than the actual bottom part of the funnel.”
Joint Interview with Expedia guys (Phocuswright Europe, 5/22/17), Phocuswright Conference
Cyril Ranque, President, Lodging Partner Services, Expedia Inc., Expedia
(on providing technology for hotels and being a “platform company”)
“The idea is pretty simple. We’ve proven that we can take the platform from our brand and power other brands very effectively in the OTA space and now the idea is to take the same platform and leverage it for hotel partners and allow them to access all the benefits of that technology…and the thinking is if we are improving the customer experience regardless of where the customer wants to book, be it on Expedia or hotels.com or on brand.com…that translates into more disposable income spent on travel. It should be good for the industry and if we power all these parts of the ecosystem, we’ll get a share of the revenue…hotels have needs for pricing, they need data to price correctly. We provide them access with competitive data, market demand, etc. so they can do their pricing, it can be a chain or individual hotel, we can provide data that a small hotel would not have access to to optimize their pricing.
Then, after they’ve done their pricing, they need to attract consumers to their website…we launched a product that allows them to spend their marketing to attract consumers from Expedia and hotels.com directly to their website, which was unthinkable a few years ago…and then the next step is powering their website to make it more effective and increase their conversion. We’re doing this with Marriott on vacations and Vacations by Marriott has grown tremendously…then after that you get to the guest experience, we’ve invested in a company called Alice in which we have a minority share which optimizes hotel operations. We also allow hotels to sign up more loyalty members…we did a test with Red Lion. Then we provide real time feedback to increase the customer satisfaction by treating problems that arise on property before customers write a review later on.”
Booking.com Executive Interview – Phocuswright India 2017 (3/13/17), Phocuswright Conference
Oliver Hua, Managing Director, APAC, Booking.com
“Three years ago we had less than 3,000 hotel partners in India. Now, today we have over 20,000. And the number of room nights per partner remains roughly steady…it’s pretty significant but we’re still in early stages of growth. We’re seeing high double-digit growth for multiple years now and we expect that to continue.
Our strategy in China is two-fold. We develop our own business, China is a major source market for us. The majority of APAC destinations – Japan, Korea, Thailand – are quite dependent on Chinese inbound. We have nearly a thousand people working in our call center in Shanghai. Then the second prong of our strategy is the partnership we have with Ctrip that evolved from a commercial partnership where they were a distribution partner for us into an equity partnership in which we invested pretty heavily into the company in 2014 and 2015…Ctrip has been leading industry consolidation in China, they’ve been rolling out new product and services…and the fact that they’re gaining share in the market is helping us as well because through them we just get a larger audience for our inventory. Our relationship with agoda, our sister company, is very similar to how we work with Ctrip in China. They are two separate brands that operate completely independently of each other.”
(on the long tail of properties)
“In Japan, it’s a well known fact that we have a situation where the market is essentially undersupplied from a traditional hotel accommodation perspective, and then you have a lot of long-tail properties that’s unoccupied because of the shrinking population. The demographic change and migration to large cities…you have a lot of apartments, short-term rentals that’s available for rent and that’s a market we’re definitely very much committed to. We actually have plenty of that type of inventory that’s available on our site for instant booking and immediate confirmation. That’s how we differentiate from other offerings. When you come to booking.com and you book a long-tail property, the customer experience is exactly the same as booking a traditional global chain hotel.”
a16z Podcast (10/28/17; B2B2C Business Models — Trick or Treat?)
Martin Casado
“One of the biggest mistakes I see is ‘listen, we’re working with system integrators, we’re working with MSPs [managed service providers] because they somehow think that’s going to give them reach to a bunch of customers, basically it never pans out…in mature markets it sometimes pans out, but in pre-chasm markets, I don’t think it ever does. [Pre-chasm meaning] there’s no market category, there’s no budget, the customer isn’t educated about what you’re doing. And the reason it doesn’t work out is because…a lot of the enterprise actually purchases from a reseller, not from the vendor directly…and the thing is [resellers] don’t have the salesforce to carry pre-chasm products. They’re good at distributing things where there’s a known budget, but if you’re doing something fundamentally new, there’s no way that a VAR can pitch, educate the customer, and so forth, so normally you have to create a pull-based market before you can actually engage partners.
In the enterprise, the two ends are the vendor, which creates the technology, and the customer, which consumes the technology. In a direct sales model, the vendor creates a sales team and the sales team shows up to the customer and manages that customer. So, let’s say you create a widget in a mature market, so the customer doesn’t have to be educated. And you’re able to get a general partner to sell it. One of the big problems is you don’t have a relationship with the customer. So much of enterprise dynamics come from renewals, expansions, and upsells. Often hyperlinearity in growth comes from expansions, so you actually have to have a relationship with the customer in order to do that. And so going that route is fraught with peril for startups. You are not the one that is actually bringing the product to the end customer…you don’t know what they want, you don’t know what they need, and you won’t have the leverage point to expand that sale […]
The biggest jump in operational complexity a start-up will ever do is when it goes from one product to two products. So, if you do introduce a second product, if you can align it with the same constituency, the same buyer, that’s the best…a natural response of start-ups of not having product/market fit is building another product, which I think is probably the worst thing you can do.
Over time, R&D pencils out as almost a fixed cost or super sublinear but sales scales linearly with people on the ground, so if you hire more sales people, they’re very expensive but to get more dollars you need more sales people. So, there’s this dream that you can have somebody else bare that cost for you…the problem is that the channel doesn’t have the salesforce to push what you’re doing…the lifecycle that normally works is the startup tries that, figures out that it doesn’t work, but maintains relationships with these channel providers. Start-up then builds a direct salesforce and creates awareness in the market and starts to sell it. Once you’ve started to sell it, you’ve actually created now a market and the market isn’t a product market but a market of services around your product. So I sell something to the enterprise just to do a proof-of-product, requires some implementation, and often companies will pay for that, and then after you’ve sold it, that requires professional services along with it. Once you’ve sold enough gear, those markets arise and now you have something you can incent a channel partner with….so now you actually have a market to incent them to invest in training, to get a relationship with the customer, etc.
It’s incumbent on the startup to create the market and once you’ve created the market, you have sufficient leverage to turn on the channel.”
Alex Rampell
“The other challenge with B2B2C is that if your C at the end is coming from the B in the model, then the two business models endanger one another. There’s a company called Yodlee, it’s been around for around 20 years, it’s a key part of the ecosystem for every fintech company that gets data from banks. So if you ever go to E-Trade and it says ‘log into your Bank of America account to wire funds’, that’s going through Yodlee. It turns out they get all of that information in aggregate and they have a different business model which is they sell anonymized aggregated information that they’re collecting from everybody, all the businesses they are working with Yodlee. If they do that too aggressively, it puts them at odds with their core, main business…you can go from being a symbiote [with your middle B] to a parasite or even an antagonist if you start doing things that are competitive with what they’re doing or hurt their primary business model.”
(when B2B2C works)
“I think Rakuten is a good example of this because if you are a bread merchant and there’s another meat merchant you can work with and you realize the meat merchant sells more meat and the bread merchant sells more bread if there’s one communal shopping mall for them all to work with, they don’t want the consumer to sign up directly, they want the consumer to sign up in that shopping mall. That’s highly symbiotic…there it’s Rakuten getting the end consumer, but those two intermediate merchants have an incentive for Rakuten to own that consumer because it makes the whole thing work.”
[CSGP – CoStar Group; REIS – Reis Inc.] Tale of Two Data Providers
Posted By scuttleblurb On In [CSGP] CoStar Group,[REIS] Reis Inc. | Comments DisabledBefore CoStar came onto the scene in 1987, getting clean and current data on rental rates, vacancies, absorption, and precedent comps needed to transact in commercial real estate was a vexing, ad hoc process. In the early/mid-90s, juniors staffed across various financial institutions devoted significant chunks of their workweeks collecting and scrubbing this information. Or […]
[TripAdvisor, Trivago, OTAs] Thoughts on the Carnage
Posted By scuttleblurb On In SAMPLE POSTS,[TRIP] Tripadvisor,[TRVG] Trivago | 1 CommentTrivago’s “relevance assessment dimension”, implemented in late 2016, is an algorithmic adjustment that compels hotel advertisers to improve their landing sites and booking engines if they want to rank higher in trivago’s search results. The idea is that while the user experience starts with a room search on trivago, it extends to when she clicks off to actually book the room on the advertiser’s site…so if the advertiser screws up that last step (according to trivago), it will have to pay more for each referral. One consequence of this change was that trivago penalized OTAs whose links sent users to yet another page of search results on OTA.com rather than directly to the property that the OTA listed on trivago.
While trivago technically has 200+ advertisers competing for placement in its marketplace, two of them, Expedia and Priceline, respectively comprise 36% and 43% of the company’s revenue. [Expedia acquired 63% of trivago from early investors in 2013 and continues to own 60% of the company post its December 2016 IPO]. It’s usually not a good idea to behave like a powerful aggregator towards two dominant customers who actually are powerful aggregators when you, actually, are not…but that’s essentially what trivago did, tasking its algorithm to extract the most value from advertisers in zero-sum fashion while providing CRM, bidding, and booking tools for smaller hotels – including “express booking” where trivago actually hosts the booking site on behalf of the advertiser – to compete more effectively against the OTA giants with the aim of stoking greater bid density and pushing the agencies, in trivago’s own words, towards “the pain points of their profitability targets.”
In the first several quarters after implementing relevance assessment, trivago saw qualified referrals ~+60% y/y and revenue per qualified referral (RPQR) growth of +4%-4.5%. The company admonished that RPQR would be lower (or, euphemistically, “normalized”) in the second half of 2017 since as advertisers adapted their sites to trivago’s relevance assessment standards, they would be not be required to bid as much for traffic. No big deal. But then things took a turn for the worse. On 9/6/17, trivago announced that revenue growth for the full year would be more like 40% instead of 50% and EBITDA would be lower than guided too, as the RPQR hit turned out to be worse than expected.
The charitable interpretation to this bleak outcome, the line that management continuously parrots to investors, is that by optimizing the user experience, trivago is nobly sacrificing near-term profits for the sake of long-term gain. Management understands that having loyal users is the key to spinning up a platform that gives you license to marginalize suppliers (advertisers, in this case), and so trivago is splurging on TV advertising [over 90% of the company’s revenue is dedicated to sales and marketing], assiduously monitoring the results, and iteratively tweaking campaigns towards the aim of building brand value. At the same time, by adjusting its bidding algorithm and forcing suppliers to play ball, it is ensuring that users have the most seamless search and booking experiences possible.
But it’s not clear to me why Trivago feels uniquely positioned to accomplish the task of creating memorable ads or whatever it is that they think drives persistent site visits. Because unlike, say, a SaaS model, where the journey from site visits to free trials to paid subscriptions sucks the user into ever deeper states of captivity that can, in theory, generate sticky, layered recurring revenue streams, what is the lock-in mechanism here? At least TripAdvisor can claim authentic and current user-generated reviews. Google began with a superior mousetrap and didn’t need to spend gobs on advertising to attract users (plus, because general search is so frequently used, it is habit-forming in a way that travel-specific search is not). Trivago’s vertical search has, well…what exactly…to keep users continuously coming back once they have clicked off the site? And furthermore, what can’t be replicated? Expedia offers its own version of relevance assessment, its Accelerator program encouraging hotel properties to graduate up the Expedia listings page by paying extra commissions or by improving quality scores.
Growth in qualified referrals and referral revenue have decelerated in dramatic fashion. No bueno:
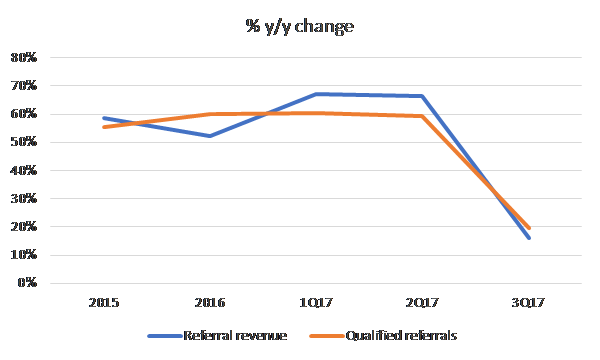
[Definition of qualified referrals from the F-1: “We define a qualified referral as a unique visitor per day that generates at least one referral. For example, if a single visitor clicks on multiple hotel offers in our search results in a given day, they count as multiple referrals, but as only one qualified referral. While we charge advertisers for every referral, we believe that the qualified referral metric is a helpful proxy for the number of unique visitors to our site with booking intent, which is the type of visitor our advertisers are interested in and which we believe supports bidding levels in our marketplace.”]
And with that, the potency of trivago’s brand advertising also appears to have waned, as the company experienced significant y/y de-leverage on sales and marketing in the latest quarter and declining returns on ad spend over the last 2 quarters:
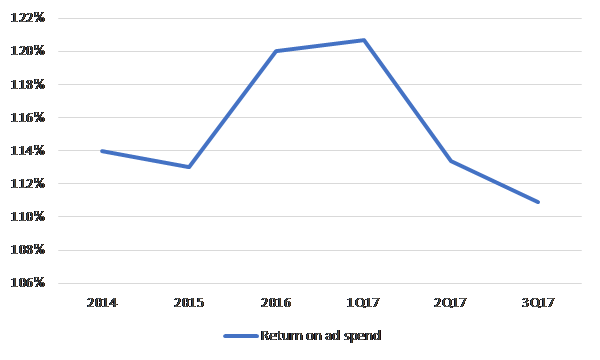
ROAS weakness also happens to coincide with TripAdvisor’s renewed commitment to brand advertising this year, so on top of volume weakness, perhaps TRVG is also witnessing pricing pressure on ad units? [After spending $51mn on TV advertising in 2015, TripAdvisor reallocated marketing dollars to online search and spent nothing at all on TV in 2016. They’re committing $70mn-$80mn this year as part of a multi-year brand ad campaign].
If online travel were fragmented up and down the value chain, then being the first to spend aggressively on brand advertising for the sake of creating a liquid marketplace that then itself becomes the value proposition, might just work. The numbers are tempting. Global online hotel bookings of ~$145bn comprise around 1/3 of the total offline + online hotel bookings and are taking share from the offline channel. At a 15% take rate, that’s a $22bn addressable market growing low double-digits annually. On its current revenue base of $1bn, claiming even a small share of that could drastically move the dial. But the question of course is, can you grab share at compelling economics? I don’t understand the fundamental value proposition offered by trivago that cannot be offered equally well by many other top-of-funnel peers or even further down-funnel for that matter.
This is why I find I Trivago’s competitive positioning so precarious: it doesn’t possess the bargaining power to procure traffic at advantaged cost nor an irreplicable process to transform that traffic into value so compelling and unique that even their powerful customers will cede economic ground. Online travel is increasingly dominated by aggregators further downstream who have myriad acquisition channels – including Facebook, Google, and direct brand advertising – through which to lure travelers. And as in any highly competitive market, attempting to generate sustainable value off brand advertising is an unwinnable game unless there is a differentiating resource at the core.
At the Citi Tech Conference last month, when asked about competitors recently copying trivago’s strategy, the company could offer only the following effete non-statement:
“I think the only sustainable competitive advantage that you can have is to continue to be ahead of your competition. And so, the competitive response is to continue to innovate in marketing and in product and make sure that there is always a gap between yourself and competitors that are copying what has worked very well for you. I think that sounds generic, but I think that’s the only thing you can do.”
TRVG’s management maintains that its can sustain 25% EBITDA margins at some point (better than Expedia’s high-teens EBITDA margins). I doubt it.
TripAdvisor is the Twitter of online travel: a unique, hard-to-replicate asset that eludes monetization but has significant strategic value. There’s clearly a double marginalization problem to be solved via vertical acquisition, which TRIP Chairman Greg Maffei seems open to. And that might really be the primary reason to hold on to the stock. Well, that, plus the non-hotel side of the business (attractions + restaurants) is killing it, growing revenue by 25%-30% over the last year and solidly profitability. That business is probably worth ~$1.5bn (4.5x revenue), leaving $2.4bn in enterprise value for a hotel business, one facing revenue and cost pressures, doing around $200mn in EBITDA (after stock comp). By comparison, trivago’s enterprise value is $1.8bn, and they’re doing only $13mn in EBITDA. The value disparity makes little sense.
[Re: “hard-to-replicate”, as I previous wrote:
“Over 360mn people visit the company’s site every month to plan their trips because they trust its deep fount of nearly 500mn authentic and current user-generated reviews and 90mn photos on 7mn hotels, attractions, and restaurants. Those travelers, upon completing their trips, post their own reviews, contributing to a burgeoning body of shared knowledge that drives traffic through better search engine rankings and compels still more potential travelers to visit Tripadvisor at the start of their research process. The company further stokes participation by offering badges and other marks of distinction to particularly helpful and active reviewers. Hoteliers, well aware of Tripadvisor’s critical top-of-funnel role, make a special effort to respond to consumer reviews. If you’ve stayed at a hotel boutique, you will have no doubt been encouraged at some point to leave a review on Tripadvisor by the hotel manager, who often proudly plasters the property’s Tripadvisor rating on the front window as a point of differentiation. It would be monstrously difficult to recreate the breadth and depth of TRIP’s reviews.”]
[“Monstrously difficult”? A bit hyperbolic on my part. In theory, I guess I don’t really see why the Priceline, which already has over 135mn hotel reviews, couldn’t expand its share as it garners more direct traffic through brand advertising]
In prior quarters, the y/y decline in TRIP’s revenue per hotel shopper was largely attributed to a mix shift from desktop to mobile, a concern alleviated by the hope that mobile monetization improvement would eventually overcome such dilution. But now, bid-downs by Priceline, which is shifting ad dollars to brand advertising after years of diminishing ROI on performance marketing, have whacked monetization on the desktop side and confounded several quarters of positively inflecting trends.
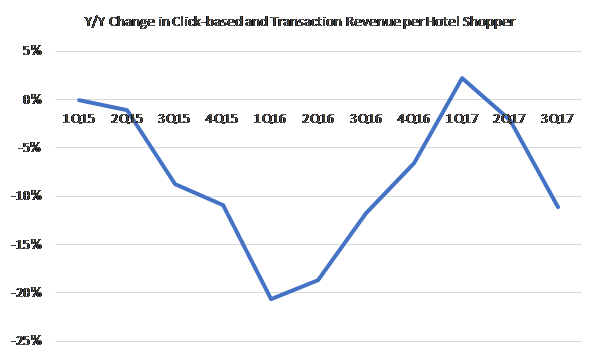
After a two-year hiatus, TripAdvisor also recently began splurging on TV advertising…so, on top of getting hosed by its largest customer on the revenue side, TripAdvisor is now competing with Priceline for TV ad spots as both pursue a common goal of driving more direct traffic to their own sites. It’s hard not to be cynical about TripAdvisor’s standalone role in the value chain.
So, with trivago implicitly raising bid prices and both trivago and TripAdvisor trying (and, in the latter case, failing) to encroach directly upon bookings, it appears that Priceline is finally saying “nuh-uh” and using bid downs as part of a bargaining tactic to keep suppliers in check. Whether the shift from performance to branded advertising is structural seems inconclusive. Recent comments from Priceline CEO Glenn Fogel:
“I think one of the things very important to recognize is the dynamic nature of how the performance marketing works. So while we can make change in terms of how much money we want to spend and we where we want to spend it, our partners are also making changes all the time, and other people and auctions are making changes. So, this is dynamic and interactive, so it’s difficult to project long term what’s going to happen.”
Still, Priceline has been talking about pressure on performance ad returns for some time and even as Expedia professes loyalty towards trivago as an acquisition channel, it admits that meta search generates lower “repeat propensity” than search engine marketing. In any case, what seems abundantly clear is that TripAdvisor and trivago, who derive 46% and 79% of revenue, respectively, from Priceline and Expedia, are really in no place to dictate terms. Generating extra-normal profits as standalone entities, like the kind implied by the obligatory “small x% of big $TAM” exhibit that these guys all like to use, requires TRIP and TRVG either claiming a fair share of extraordinary surplus or an unfair share of modest surplus. The absence of a uniquely compelling value proposition impedes the former; industry structure constrains the latter.
Implicit in my TRVG/TRIP bashing, however, is that value in the this industry accrues a level below and in that spirit, Expedia could be interesting. EXPE sold off last week as the company noted that its cost structure would be larded with investments related to accelerated hotel on-boarding [3 years ago, EXPE was adding 25k-30k hotels / year, this year it’ll be 80k, and will “step change” in future years], cloud computing [a 2-3 year transition. $100mn this year, much greater than management’s guidance a year ago, growing by over 50% next year], and marketing [as management turns its attention to deepening local marketplace liquidity after years of broad-based acquisition].
Expedia isn’t the cleanest company with the strongest moat – the core OTA is dependent on Google for traffic and faces competition from a consolidating supplier base, HomeAway is up against AirBnB, tech stack integration across a slew of acquisitions appears to have been sloppy – but as the second largest OTA by bookable properties next to Priceline, the company has certainly crossed the threshold of critical scale and fostered a sustainably profitable two-sided marketplace. Disintermediation concerns stemming from an increasingly consolidated supplier base and worries about Google/Facebook aggressively moving into the space, have plagued OTAs for years…but Priceline and Expedia have done just fine as continuous investment in technology, marketing, hotel relationships, and vigorous A/B testing have congealed into a hard-to-replicate value proposition for suppliers looking to offload inherently perishable inventory and travel shoppers looking to dependably source the broadest, most relevant selection at the lowest price, with increasing participation on each side of the platform begetting buy-in from the other.
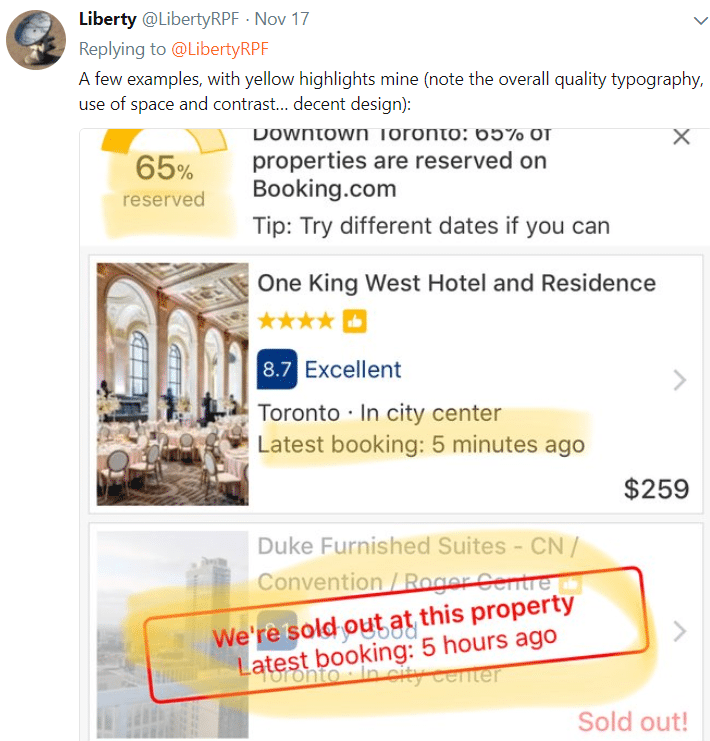
[Re: A/B testing, as one Twitter friend put it…
HomeAway, acquired for what seemed like a pricey $3.9bn in December 2015, has been growing rapidly (+40%-50% y/y) and profitably in the face of competition from AirBnB and Priceline, and now seems like a pretty smart buy. And Expedia is still in the process of making all ~100k vacation rentals available exclusively online (some bookings are currently arranged offline between guest and host) [5], and has not yet really begun to pursue international markets or fuse Homeaway listings with inventory from its core OTA sites in cities.
When I strip out trivago and stock comp (see below), it looks like Expedia is trading for around 11x EBITDA and 17x FCFE, which seems reasonable to me even if we grant that EBITDA growth will slow to the bottom end of the +10%-20% range (or even somewhat below) for the next few years on accelerated spending…and it looks quite cheap if we think that by weaning itself off acquisitions, dedicating itself to organically deepening engagement, broadening the platform through aggressive on-boarding, and boosting overall productivity by partly shifting its tech infrastructure to the cloud, Expedia can drive accelerated bookings growth and margin expansion 3 years out. At the very least, I think we can be far more confident that Expedia’s investments offer a reasonable return than that trivago’s continuous spending on TV commercials will ignite sustainable platform activity.
($ millions except per share data)
| EXPE TEV ex. TRVG cash | 19,159 |
| TRVG stock price | $ 7.17 |
| x # TRVG shares owned by EXPE | 209 |
| = | 1,499 |
| Adj. EXPE TEV | 17,661 |
| EBITDA ex. TRVG | 1,589 |
| multiple | 11.1x |
| FCFE ex. TRVG | 1,249 |
| Stock comp ex. TRVG | 135 |
| EXPE FCFE ex. TRVG ex. stock comp | 1,114 |
| /share | $ 7.06 |
| multiple | 17.4x |
You can also own Expedia through Liberty Expedia (LEXEA), which owns 15.5% of Expedia’s common stock representing a 51.9% voting interest in Expedia…but, I don’t think there’s a compelling “arb” here. LEXEA split off from Liberty Ventures a year ago for the purpose of Expedia eventually purchasing LEXEA’s EXPE shares. Liberty Expedia also owns an internet retailer of health and dietary supplements called Vitalize (formerly known as Bodybuilding.com), which, based on declining revenue and profits, isn’t doing so hot, and has deteriorated to such an extent that it is small enough to be unceremoniously lumped into “corporate and other”. It does around $316mn in trailing revenue with negligible OIBDA.
You are getting 0.41 shares of EXPE for every 1 share of LEXEA that you own. LEXEA also has around $5.40 in net debt / share. So the NAV breaks down like this…
| NAV | |
| Expedia | $ 50.43 |
| Net debt | $ (5.36) |
| Vitalize | ??? |
| Total | $ 45.07 |
…vs. LEXEA’s current share price of $46. The delta between NAV and the LEXEA share price values Vitalize at around 0.2x trailing revenue. Seems fair. Whatever.
Priceline’s stock also sold off post-earnings on decelerating bookings (from ~mid-20s y/y ex. fx growth over the last 4 quarters to 16% in the latest quarter). While size constraints may translate into slower growth relative to the past, there’s plenty of runway ahead. Its largest online property, Booking.com, has an insurmountable moat in a fragmented European market [in Europe, independent lodging comprises 67% of total rooms vs. 30% in the US] where I estimate it claims around 40% of European online accommodation bookings, or about 20% of total European bookings. Globally, Priceline’s ~$80bn of total gross bookings is just 20% of online hotel bookings, or about 6%-7% of total online + offline. Room nights +19%, the number of bookable properties +41% (including vacation rentals +58%) during the most recent quarter, and the meta properties, Kayak and (more recently) Momondo, are growing and profitable. OpenTable, on which the company took a huge impairment charge last year, has sucked, but I think we’re past that. I don’t see any meaningful impediments to Priceline continuing to grow its cash earnings per share by mid-teens+ for the foreseeable future.
So yea, setting aside the takeout aspect for TripAdvisor and just evaluating these companies on their standalone long-term value creation potential, I would rather own Priceline (17x EBITDA backing out long-term investments, including Ctrip) or Expedia (11x), respectively, than either Trivago (NM) or TripAdvisor (17x).